By Jorge L. Contreras*, Rohini Lakshané**, Paxton M. Lewis***
Download a PDF version of this article here
Introduction
In
2012, Natco Pharma Ltd. (“Natco”) petitioned the Indian Patent Office (“IPO”)
for a compulsory license to manufacture Bayer’s patented cancer drug, Nexavar.[1]
Natco cited numerous grounds in support of its petition, including Nexavar’s
high cost and limited availability in India.[2] But along with these relatively common
complaints in the global access to medicines debate,[3]
Natco raised a less typical theory; Bayer failed to “work” the patent
sufficiently in India.[4] In doing so, Natco invoked a seldom-used
provision of Indian patent law that allows any person to seek a compulsory
license under an Indian patent that is not actively being commercialized by its
owner within three years from the issuance of the patent.[5]
Patent
working requirements exist in different forms throughout the world. Broadly
speaking, to “work” a patent is to practice, in some manner, the patented
invention within the country that issued the patent. While patents are seen as
a means to create incentives for inventors to share their ideas, working
requirements are intended to mitigate the exclusivity of patent monopolies by
requiring the patent holder to disseminate its invention into the local market.[6]
The patent holder thereby imparts knowledge and skills to the local community,
enhances economic growth, supports local manufacturing, and promotes the
introduction of innovative new products into the local market.[7]
While
patent working requirements have existed in various jurisdictions for more than
a century, working requirements have seldom been the subject of vigorous
enforcement.[8] The U.S.-Brazil dispute and the Natco case
represent a revival of interest in patent working requirements. In particular,
the Natco case has reintroduced
questions of whether working requirements are, or should be, allowed under the
TRIPS Agreement.
In
prior work, Contreras and Lakshané have analyzed the domestic Indian patent
landscape pertaining to mobile device technology.[9]
The authors now extend that work to examine the working of those patents. This
Article presents a detailed case study of the Indian patent working statutes
and their procedures, particularly the requirement that all patent holders file
an annual form (Form 27) to demonstrate that their patents are being worked in
the country. We collected and reviewed all publicly available Forms 27 in the
mobile device sector to assess the completeness and accuracy of the information
disclosed. We then analyzed the results to assess the robustness of India’s patent
working requirement and its utility for complex information and
communication-based products and technologies.
The remainder of
this Article proceeds in four principal parts. Part I.A provides a brief
history of patent working requirements. Part I.B describes the development of
India’s current working requirements and its novel Form 27 filing requirement.
Part II describes our empirical study of India’s Form 27 filings in the mobile
device sector. Part III discusses our findings and analysis. We conclude with
recommendations for further study and policy.
I. Patent Working Requirements
A. History of Patent Working Requirements
The
origins of patent working requirements have been traced to the 1300s, when
early patent privileges were granted in jurisdictions such as feudal England
and the Republic of Venice, with an expectation that foreign innovators would
teach the invented art to local industry.[10] The underlying incentive for providing
monopoly rights was thus tied to local industrialization.[11]
This incentive to share technology was directed not only to local citizens but,
even more so, to foreign inventors.[12] Countries issued patent privileges to
encourage foreigners to migrate and develop or protect local industry by
teaching their art to the local population.[13] Local industrialization was thus considered
a central means to economic development and technological advancement.[14]
Despite
these early developments, by the late 19th and early 20th centuries, developed
countries’ conceptual understanding of a patentee’s obligation and its
relevance to national development began to shift away from local manufacturing.[15]
As a result, in many developed countries disclosure through importation became
sufficient to meet the “informational goal” of patents, particularly patents
that represented improvements to existing technologies.[16]
The 1883 Paris
Convention for the Protection of Industrial Property prohibited the automatic
forfeiture of a patent for a failure to work it locally.[17] While both developed and developing countries
disputed the proper remedy for the failure to work a patent, there remained a
consensus that failure to work a patent was inconsistent with the patent
privilege.[18]
A
half-century later, the 1925 Hague Conference, which amended the Paris
Convention, recognized the failure to work a patent as an abuse that member
states could “take necessary legislative measures to prevent.”[19] As a remedy for non-working, drafters viewed
compulsory licensing of non-worked patents as more palatable than outright forfeiture.[20] Nevertheless, forfeiture of patent rights
was still permitted under the Convention, though an action for forfeiture could
not be brought until two years following the issuance of the first compulsory
license covering the non-worked patent.[21]
In the 1967 Stockholm amendments to the Convention, further limitations on
compulsory licensing for non-working patents were introduced, notably
prohibiting member states from permitting the grant of a compulsory license for
failure to work until three years after the issuance of the allegedly
non-worked patent.[22]
Within the
flexibilities allowed by the Convention, developing countries continued to
adopt strict working requirements and to resist international requirements that
favored developed countries.[23]
For example, in the late 1970s and early 1980s, developing countries proposed
revisions to the Paris Convention that would have provided that mere
importation did not satisfy local working requirements and to permit the
expansion of sanctions for non-working beyond compulsory licensing.[24]
The
desire of developed countries for stronger international rules relating to
intellectual property led to the formation of the World Trade Organization
(“WTO”) in 1994, under which the Trade Related Aspects of Intellectual Property
Rights (“TRIPS”) Agreement was negotiated.[25]
While the TRIPS Agreement does not explicitly address patent working
requirements, Article 2.1 incorporates Article 5A of the Paris Convention (i.e.
the article related to compulsory licensing and the limitations on granting
compulsory licenses discussed above), and Article 2.2 reinforces the existing
obligations of members of the Paris Union.[26] Additionally, Article 27.1 of the TRIPS
Agreement, which establishes requirements for patentable subject matter, prohibits
“discrimination as to the place of invention, the field of technology and
whether products are imported or locally produced” raising a question as to
whether countries with local working requirements must recognize importation as
an acceptable manner of satisfying those requirements.[27] However, Article 30 of the TRIPS Agreement
permits a member state to allow exceptions to the exclusive rights of a patent
holder, and Article 31 allows a state to issue a “compulsory” license under one
or more patents without the authorization of the patent holder “in the case of
national emergency or other circumstances of extreme urgency or in cases of
public non-commercial use.”[28] Given these mixed signals, commentators are
divided on whether, and how, the TRIPS Agreement may affect local working
requirements.[29]
To date, the only
WTO dispute challenging the validity of national working requirements has been
between the United States and Brazil.[30] In 2000, the Clinton administration,
responding to concerns raised by the American pharmaceutical industry,
initiated a WTO dispute proceeding to challenge Brazil’s local working
requirement.[31] The United States argued that Article 68 of
Brazil’s 1996 Industrial Property Law violated Articles 27(1) and 28(1)[32] of the TRIPS Agreement for discriminating
against U.S. owners of Brazilian patents whose products were imported, but not
locally produced, in Brazil.[33]
Despite the pending
WTO litigation, the Brazilian Ministry of Health adopted an aggressive stance
toward reducing the price of antiretroviral medications and threatened to issue
compulsory licenses for the local manufacture of two such drugs, both patented
by U.S. companies, if they were not discounted by 50%.[34] In response to political and public
pressures, the United States and Brazil settled the dispute before any
definitive opinion was issued by the WTO.[35]
B. The Evolution of India’s Patent Working Requirement
1. Background
As
a British colony, India’s pre-independence patent laws were modeled largely on
then-prevailing English law.[36] India gained its independence from Great
Britain in 1947 and almost immediately began to consider the adoption of patent
laws reflecting emerging national goals of industrialization and economic
development.[37] Thus, in early 1948, a committee known as
the Tek Chand Committee was appointed to review and reconcile India’s patent
laws with its national interests.[38]
The committee’s efforts resulted in the Chand Report, which recommended the use
of compulsory patent licenses to stimulate India’s industrial economy.[39]
A second major
report commissioned by the Indian government and prepared primarily by Shri
Justice N. Rajagopala Ayyangar, was issued in 1959.[40] The Ayyangar Report suggested that India
should deviate from the “unsuitable patent policies of industrialized nations”
because patent regimes operate differently in developing versus developed
nations.[41] Recognizing that a significant weakness in
developing nations “is that foreign patent owners do not work the invention
locally,” the Ayyangar Report recommended compulsory licensing as “the remedy
to redress the handicap of foreigners not working the invention locally.”[42]
2. The Patents Act, 1970
The India Patents
Act, 1970, was enacted in 1972.[43] Among other things, it sought to address the
economic repercussions resulting from foreign dominance of the patent landscape
in India, as recommended by the Chand Report and the Ayyangar Report.[44] Accordingly, Section 83 of the 1970 Act
provides certain policy-driven justifications for India’s working requirements,
explaining:
“that patents are
granted to encourage inventions and to secure that the inventions are worked in India on a commercial scale
and to the fullest extent that is reasonably practicable without undue delay;
[and]
that they are not
granted merely to enable patentees to enjoy a monopoly for the importation of the patented article[.]”[45]
These provisions
make clear that working a patent in India is both an important policy goal and
consists of something more than importation of the patented article into India.
Some additional knowledge transfer must occur so that manufacturing of other
steps necessary for commercialization are carried out in India.
Following the
Ayyangar Report’s recommendations, Section 84(1) of the 1970 Act provided for
compulsory licensing of patents as follows:
“At any time after
the expiration of three years from the date of the sealing of a patent, any
person interested may make an application to the Controller[46] alleging that the reasonable requirements of
the public with respect to the patented invention have not been satisfied or
that the patented invention is not available to the public at a reasonable
price and praying for the grant of a compulsory licence to work the patented
invention.”[47]
These requirements,
particularly the availability of the patented article to the public at a
“reasonable price,” seek to address issues raised in the debate over access to
medicines, and particularly the high pricing maintained by many Western
pharmaceutical firms in developing countries.[48]
However, working of
patents more generally is incorporated into the compulsory licensing regime
through Section 90, which clarifies when the “reasonable requirements of the
public” will be deemed not to have been satisfied.[49] In particular, Section 90(c) specifies that,
for purposes of compulsory licensing under Section 84, “the reasonable
requirements of the public shall be deemed not to have been satisfied Ö if the
patented invention is not being worked in the territory of India on a
commercial scale to an adequate extent or is not being so worked to the fullest
extent that is reasonably practicable[.]”[50] Thus, local working of patents is tied to
the public interest and has become express grounds for requesting a compulsory
license in India.
In addition to
giving applicants the right to seek a compulsory license under non-worked
patents, the 1970 Act also gave the Controller the power to revoke a patent on the grounds that the
reasonable requirements of the public were not being satisfied or the patented
invention was not available to the public at a reasonable price.[51] Under Section 89(1), any interested person
could apply to the Controller for such an order of revocation no earlier than
two years following the grant of the first compulsory license under the
relevant patent.[52]
3. India’s Current Working Requirement
India
became a member of the World Trade Organization on January 1, 1995, also making
India a party to the TRIPS Agreement.[53] In order to reconcile the 1970 Act with the
TRIPS Agreement, India amended its Patents Act in 1999, 2002, and 2005.[54] Most relevant to this Article, the 2002
amendments modified India’s compulsory licensing and working requirements.[55]
India’s amended
Patents Act retains strong working requirements, which permit the Controller to
revoke unworked patents.[56] Section 83 of the Act, as amended in 2002,
provides several additional justifications for India’s patent working
requirement not contemplated in earlier versions of the Act. For example, the
2002 amendments recognize that patents are intended to support the “transfer
and dissemination of technology . . . in a manner conducive [sic] to social and
economic welfare.”[57] Several of the new justifications emphasize
that patents should support, and not impair, the public interest, particularly
“in sectors of
vital importance for socio-economic and technological development of India.”[58]
Against this
backdrop, the amended Act explicitly makes compulsory licenses available for
non-worked patents. Section 89 explains that one of the “general purposes” of
compulsory licenses is to ensure that “patented inventions are worked on a
commercial scale in the territory of India without undue delay and to the
fullest extent that is reasonably practicable.”[59] The amended Act expanded Section 84(1),
which authorizes third parties to seek compulsory licenses, to include as an
express basis for seeking a compulsory license “that the patented invention is not worked in the territory of
India.”[60]
Thus, new section
84(1)(c) establishes working of a patent as an independent ground for seeking a
compulsory license, in addition to the grounds under sections 84(a) and (b)
that the patented technology fails to reasonably meet public needs. This
approach contrasts with the original 1970 formulation, discussed above, in
which non-working of a patent formed a basis for seeking a compulsory license,
but only as an element of the “reasonable requirements of the public,” rather
than an independent ground in itself.[61]
Section 84(6)
specifies factors that the Controller must take into account when considering
an application for a compulsory license, including:
(i) the nature of the invention, the time which
has elapsed since the sealing of the patent and the measures already taken by
the patentee or any licensee to make full use of the invention;
(ii) the ability of the applicant to work the
invention to the public advantage;
(iii) the capacity of the applicant to undertake
the risk in providing capital and working the invention, if the application
were granted;
(iv) as to whether the applicant has made efforts
to obtain a licence from the patentee on reasonable terms and conditions and
such efforts have not been successful within a reasonable period as the
Controller may deem fit [i.e., not ordinarily exceeding a period of six months] . . . . [62]
Section 84(6)
appears to represent a concession to patent holders, making clear that
compulsory licenses will only be granted to applicants that are able to exploit
the licensed patent rights in a manner that is likely to remedy the failure of
the patent holder to work the patent.
While
a formal definition of working is not provided under the statute, the language
of section 83 suggests that the patented invention must be manufactured locally
to the extent possible and that importation would be acceptable only if local
manufacturing is unreasonable.[63]
Additionally, the statutory language suggests that if importation is necessary,
only the patent holder or its chosen licensees may import the patented
invention.[64] The statute also fails to establish any
circumstances that may be excused from India’s patent working requirement. This
omission may have been intentional, perhaps suggesting that any technology that
is worth patenting in India should also be capable of being worked in India.
In short, India’s
patent working requirement is intended to be taken seriously. The penalties for
failing to work a patent include the issuance of a compulsory license beginning
three years after patent issuance, and if that does not fulfill public
requirements for the patented article, possible revocation of the patent. Moreover,
there is evidence that Indian courts may be reluctant to grant injunctive
relief to patent holders that do not work their patents.[65]
C. The Indian Working Requirement and Natco
Pharma Limited v. Bayer Corporation
India’s
patent working requirement was featured prominently in Natco’s recent
compulsory license request with respect to Bayer’s Indian patent covering
sorefanib tosylate, a kidney and liver cancer drug marketed by Bayer as NexavarTM.
Bayer obtained an Indian patent covering Nexavar in 2008.[66] Despite Bayer’s estimate that more than
8,800 patients in India were eligible to take the drug, its imports were
sufficient to supply only 200 patients.[67] Moreover, Bayer priced a monthly dose of the
drug at more than 280,000 Rupees (approximately US$5,608), a price unaffordable
to the vast majority of Indians.[68] In response, Natco, an Indian generic drug
manufacturer, attempted to negotiate a license with Bayer to manufacture and
sell Nexavar in India.[69] However, when negotiations were
unsuccessful, Natco applied to the Drug Controller General of India for
regulatory approval to manufacture a generic version of Nexavar in India.[70] The approval was granted.[71]
Natco then
petitioned the Controller of Patents under section 84 of the Patents Act for a
compulsory license to manufacture a generic version of Nexavar.[72] Natco offered several justifications in
support of its application for a compulsory license, including Nexavar’s high
cost and limited availability in India.[73] In addition, Natco argued that Bayer had
failed to work its patent in India within three years of its issuance, as
required under section 84(1)(c) of the Patents Act. Specifically, Natco argued
that “[t]he patented product is being imported into India and hence the product
is not worked in the territory of India to the fullest extent that is
reasonably practicable.”[74] Additionally, Natco argued that Bayer faced
“no hurdle[s] preventing [it] from working the Patent in India” because Bayer
already had “manufacturing facilities in India for several products.”[75]
Bayer responded that
it actively imported Nexavar into India, which demonstrated sufficient working,
and argued that India’s working requirement did not require manufacture of the
patented product in India.[76] In evaluating Natco’s petition, the
Controller considered the legislature’s intent, the Paris Convention, the TRIPS
Agreement, and India’s Patents Act.[77] In view of these authorities, the Controller
interpreted the term “worked” to mean that the patented invention must be
manufactured or licensed within India, reasoning that “[u]nless such an
opportunity for technological capacity building domestically is provided to the
Indian public, they will be at a loss as they will not be empowered to utilise
[sic] the patented invention, after the patent right expires.”[78] Under this interpretation, the Controller
concluded that Bayer had not worked its patent in India since importation is
not sufficient to constitute “working” a patent.[79] Accordingly, in 2012 the Controller issued a
compulsory license to Natco under Bayer’s patent covering Nexavar.[80]
Bayer
unsuccessfully appealed the Controller’s decision to the Indian Intellectual
Property Appellate Board (IPAB).[81]
The IPAB affirmed the Controller’s decision, but disagreed with the Controller’s
interpretation of the term “worked.”[82] Instead of ruling that working categorically
excludes importation of the patented product into India, the IPAB concluded
that determining whether a patented invention is worked must be considered on a
case-by-case basis.[83] Thus, the term “worked” does not necessarily
exclude importation, but it also does not strictly require manufacturing in
India.[84]
In affirming the
decision of the IPAB, the Bombay High Court opined that “[m]anufacture in all
cases may not be necessary to establish working in India[.]”[85] However, the court implied that working a
patent without local manufacture
could be a high hurdle to clear, reasoning that the patent holder must then
“establish those reasons which makes it impossible/prohibitive for it to
manufacture the patented drug in India.”[86] It is only when the patent holder satisfies
the authorities that “the patented invention could not be manufactured in
India” that it can be considered worked by import.[87]
Apart from the
working requirement, the Bombay court focused on whether Bayer had reasonably
satisfied the requirements of the public, recognizing that those requirements
might differ depending on the type of product covered by the patent.[88] Thus, when assessing whether demand for the
patented article was met to an “adequate extent,” the considerations
pertaining, for example, to a luxury article would vary significantly from
those pertaining to a lifesaving medicine. In the case of medicines, the court
reasoned, meeting public demand to an adequate extent should be deemed to mean
it is available to 100% of the market: “Medicine has to be made available to
every patient and this cannot be deprived/sacrificed at the altar of rights of
[the] patent holder.”[89]
Following Natco’s
successful application for, and defense of, its compulsory license, other
generic drug manufacturers sought compulsory licenses to manufacture patented
pharmaceutical products in India. For example, in 2013, BDR Pharmaceuticals,
Ltd., an Indian manufacturer, filed an application for a compulsory license to
manufacture Bristol Myers Squibb’s anti-cancer drug dasatinib (marketed as
SprycelTM),[90] and the Indian Ministry of Health
recommended that the Department of Industrial Policy and Promotion (DIPP) grant
local manufacturers compulsory licenses for trastuzumab, a breast cancer drug
marketed by Roche (HerclonTM) and Genentech (HerceptinTM)
and ixabepilone (Roche’s IxempraTM).[91] To date, each of these petitions has failed
for various reasons other than that pertaining to dasatinib, which remains
under consideration by DIPP.[92]
D. Form 27 and India’s Reporting Requirement
The Indian patent
working requirement under Section 84 of the Patents Act, as well as the
availability of compulsory licenses for non-worked patents, is not unique to
India, and other developing countries have adopted similar legal requirements.[93] India has, however, enacted what appears to
be a unique reporting structure associated with its patent working requirement.[94] India adopted a form submission requirement
as a means to regulate the patent working requirement under the India Patents
Act in 1970.[95] Specifically, section 146(2) of the Patents
Act provides that:
every patentee and
every licensee (whether exclusive or otherwise) shall furnish in such manner
and form and at such intervals (not being less than six months) as may be
prescribed statements as to the extent to which the patented invention has been
worked on a commercial scale in India.[96]
In support of this
statutory requirement, the patent rules adopted by the Indian Ministry of
Commerce and Industry provide that the required statements of working must be
submitted in a prescribed format (Form 27).[97] The rules also provide that such statements
must be furnished to the Controller of Patents in respect of every calendar
year within three months following the end of such year.[98]
Form 27, a template
of which is appended to the 2003 version of the Indian patent rules, requires
the patent holder to disclose “the extent to which the patented invention has
been worked on a commercial scale in India.”[99] To that end, Form 27 requires that the
patent holder complete the following information:
The patented
invention:
(i) { } Worked { } Not worked [Tick (✓) mark the relevant box]
a. if not worked:
reasons for not working and steps being taken for the working of the invention.
b. if worked: quantum
and value (in Rupees), of the patented product:
manufactured in India
imported from other
countries (give country wise details)
(ii) the licenses and
sub-licenses granted during the year;
(iii) state whether the public requirement[100] has been met partly/adequately/to the
fullest extent at reasonable price.[101]
Under Section 122,
failing to submit a Form 27 or providing false information on the form may lead
to a significant fine, imprisonment, or both.[102]
Though
India’s working requirement first appeared in the Patents Act in 1970, it
appears to have been ignored until around 2007. In 2007, the Controller first
mentioned the local working of patented inventions in his annual report.[103] The reports provided by the Controller
between 2007 and 2009 indicate that, on average, less than 15 percent of Indian
patents were being worked commercially.[104] In 2009, 2013 and 2015, the Controller
issued public notices calling on patent owners to comply with their obligations
to file statements of working on Form 27.[105]
While
the penalties for failing to furnish information via Form 27 are steep,
potentially resulting in fines or imprisonment,[106] local critics claim that many patent holders
fail to make the required filings and that the Indian government has never
taken meaningful action to penalize this non-compliance.[107]
On
February 12 2013, the Indian Patent Office announced plans to make Form 27
submissions for the year 2012 available to the public via the IPO website.[108] As discussed in Part II.A below, that effort
has been met with limited success.
E. Theory and Criticism of Form 27
There is little
legislative or administrative history explaining the genesis of India’s unique
Form 27 requirement. On one hand, a requirement that the details of patent
working be disclosed by patent holders supports the goal of making unworked
patents available for compulsory licensing in India, both to promote economic
development and public access to patented products. A public registry of Forms
27 could also shift enforcement of India’s working requirement from the IPO and
Controller to private sector entities with the greatest incentive to monitor the
working of patents in their respective industries. This shift could relieve
India’s resource-strapped administrative agencies of a potentially significant
policing function, one that it does not appear they were actively enforcing in
any event.
However,
it is not clear that these goals are well served by the current Form 27
framework, which has been criticized by a number of local commentators.[109]
For example, the IPAB ruled in Natco
that the term worked must be decided on a case-by-case basis. How, then, should
patent holders answer the first question posed in Form 27 and its
sub-questions? How is a patent holder to know whether importation or licensing
in a certain case will qualify as working a patent in India? If the Form is
intended to increase transparency and certainty regarding the working of
patents in India, it is hindered in so doing by the lack of a formal definition
of working. This lack of clarity affects both patent holders, who are less able
to order their affairs so as to comply with statutory working requirements, as
well as potential compulsory licensees, who lack a clear assurance of when a
compulsory license petition will be successful.
Commentators have
raised a variety of additional critiques of the Form 27 framework. The
U.S.-based Intellectual Property Owners Association, in a formal 2014
submission to the U.S. Trade Representative, has referred to the Form 27
process as “highly burdensome” and warns that the information disclosed in
publicly-accessible forms could “result in even greater pressure on Indian
authorities to compulsory license [patented] products.”[110] Moreover, the association argues that Form
27 does not adequately recognize that some patents may be practiced by multiple
products, or that multiple patents may be practiced by a single product.[111] Thus, it may be unrealistic for patent
holders to attribute a “specific commercial value” to specific patented
features of complex technologies.[112]
Additionally, a
number of Indian practitioners have raised concerns that the public disclosure
of confidential plans for working patents through Form 27 may jeopardize or
destroy valuable trade secrets and proprietary information.[113] This threat could cause patent holders to
disclose as little specific or valuable information as possible in their Form
27 filings, a result that is suggested by the findings discussed in Part III
below.
Based on studies of
filed Forms 27, Professor Shamnad Basheer,[114] has concluded that India’s local working
Form 27 submission requirements are not being taken seriously, particularly by
international pharmaceutical companies.[115] As a result, in 2015 Professor Basheer
initiated public interest litigation in the High Court of Delhi against the
Indian government for failure to comply with India’s patent laws.[116] The suit seeks a judicial order compelling
the Indian government “to enforce norms relating to the disclosure of
‘commercial working’ of patents by patentees and licensees” and to take action
“against errant patentees and licensees for failure to comply with the
mandate.”[117] In 2016 an Indian patent attorney, Narendra
Reddy Thappeta, filed an application to intervene in Basheer’s public interest
suit, among other things, in order to raise issues regarding the difficulty of
complying with Form 27 requirement for information and communication technology
providers.[118]
Despite its
perceived problems, Form 27 has proven useful in Indian proceedings. Notably,
the information disclosed in Bayer’s Form 27 filings played an important role
in the Natco case by helping to
establish the low number of patients having access to the drug.[119] Basheer refers to the working requirement as
“a central pillar of the Indian patent regime” and views the disclosure
requirements of Form 27 as essential tools to ensure that needed information is
made public.[120]
II. Empirical Study of Indian Form 27 Disclosures in the Mobile Device Industry
In order to gain a
better understanding of India’s patent working requirement, particularly patent
holders’ compliance with the statutory requirement to declare information about
the working of their patents through Form 27, we conducted an empirical study
of all available Form 27 submissions for Indian patents in the mobile device
sector. In this Part, we describe the objectives, background and methodology of
this study.
A. Background: Existing Data and Studies
Every year, the
Controller publishes an Annual Report containing statistics relating to patent
filings in India. Since 2010, this report has contained data relating to Form
27 filings. This data indicates that a significant number of patent holders
fail to file Form 27 as required. Below is a summary of this data as derived
from the Controller’s Annual Reports from 2010 to 2016:
Table 1
Indian Controller of Patents Form 27 Filing Data (2010-2016)
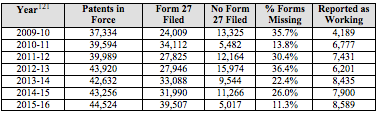
Under the Patents
Act, a Form 27 must be filed every year with respect to every issued patent in
India. Accordingly, the discrepancy between the number of patents in force for
a given year and the number of Forms 27 filed likely indicates non-compliance
with the filing requirement. Interestingly, it appears that instances of
non-compliance dropped noticeably in years immediately after the Controller
issued its public reminders to file Form 27 in December 2013, February 2013 and
early 2015.[122] Even so, compliance has not been complete
even in these years.
As noted above,
Professor Shamnad Basheer has conducted two studies of Form 27 compliance in
India. The first study, released in April 2011, focused on the pharmaceutical
sector.[123] The researchers selected seven
pharmaceutical products directed at either cancer or hepatitis, all of which
were subject either to Indian litigation or patent office oppositions and were
patented in India between 2006 and 2008. They then collected Form 27 filings
relating to each of these patents through a series of Right to Information
(RTI) petitions to the Indian Patent Office (IPO).[124] Based on the Forms produced by the IPO in
response to these requests, the researchers found significant non-compliance
with Form 27 filing requirements: some firms failed to file forms in some
years, while some forms that were filed were incomplete.[125]
Professor Basheer’s second
study had a broader scope, covering a total of 141 patents: 52 patents held by
13 firms in the pharmaceutical sector, 52 patents held by 7 firms in the
telecommunications sector, and 37 patents held by 4 institutions which are
claimed to have arisen from publicly-financed research.[126] The researchers used series of RTI petitions
to collect a total of 263 Forms 27 corresponding to these patents filed between
2009 and 2012.[127]
Based on a total of
141 patents, full compliance with Form 27 filing requirements would have
yielded 423 Forms 27 over the three-year period studied. The total of 263 Forms
identified indicates a non-compliance ratio of approximately 38%,[128] assuming that all filed forms were produced
by the IPO. A review of the reported data[129] indicates that some firms, particularly in
the pharmaceutical sector, were assiduous in filing Forms 27. For example,
Genentech and Janssen Pharmaceuticals, with two patents each, each filed six
Forms 27, suggesting full compliance. Other firms, however, fell far short of
this measure. Apple, for example, with four patents, filed only one Form.
In addition to raw
filing statistics, Prof. Basheer investigates the quality of the disclosures
made in individual Forms 27. He finds that significant numbers of filed Forms
“were grossly incomplete, incomprehensible or inaccurate.”[130] For instance, numerous forms failed to
indicate how patents were being worked or the quantity, value or place of
manufacture of patented products as required by the Form.[131] In addition, of forty-two Forms that
disclosed non-working of a patent, twenty-eight (65%) failed to offer any
reason for non-working.[132] Though the raw data underlying these
conclusions does not appear to be publicly available, choice excerpts from a
few Forms are offered.
While the prior
studies cited above suggest that there are substantial non-compliance issues
with Form 27 practice in India, additional data is required to develop a more
complete understanding of this issue. The Controller’s annual report data is
provided only at a gross level and lacks any detail regarding compliance. Prof.
Basheer’s pioneering studies, while first alerting the public to the problems
of non-compliance, cover only small, non-random samples of patents and end
prior to the general online availability of Forms 27.
B. Methodology
In this study, we
sought to assess annual Form 27 submissions across a comprehensive set of
patents and a substantial time frame. To do so, we utilized a set of 4,052
Indian patents identified by Contreras and Lakshané as of February 2015 in a
prior study of the Indian mobile device patent landscape (Landscape Study).[133] Another 367 patents pertaining to mobile
device technology, which were not included in the original Landscape Study,
were also identified by an independent contracted search firm. In the
aggregate, we analyzed 4,419 Indian patents issued as of February 2015 in the
mobile device sector, which we believe to represent the large majority of
issued Indian patents in this sector as of the date selected.
We identified Form
27 filings with respect to each such patent through searches[134] of two public online databases maintained by
the Indian Patent Office: Indian Patent Advanced Search System (“InPASS”) and
Indian Patent Information Retrieval System (“IPAIRS”).[135] We manually eliminated duplicate results
obtained from these two databases.
Our initial searches
in 2015 yielded Form 27 submissions for only 1,999 out of 4,419 patents. These
searches yielded no Forms 27 for some firms known to be significant patent
holders in the mobile devices industry. To attempt to locate the missing forms,
Lakshané, through the Centre for Internet and Society (CIS), submitted two
formal requests to the IPO located in Mumbai under the Indian Right to
Information (“RTI”) Act of 2005. The first RTI application was submitted on
June 10, 2015, requesting Form 27 information for over 800 patents.[136] On June 17, the IPO replied with generic
instructions on how to find Form 27 submissions online.[137] A second RTI application was filed on March
11, 2016.[138] The second request sought Form 27 filings
pertaining to 61 of the remaining patents.[139] These 61 patents were selected to represent
a sample of patents held by the full cross-section of patent holders identified
in the Landscape Study. In April 2016, the IPO replied that, due to internal
resource constraints, it could only provide CIS with Forms 27 for eleven (11)
of the requested patents.[140]
Nevertheless, a few
days after IPO’s reply, Form 27 submissions pertaining to patents in the
Landscape Study started appearing on InPASS and IPAIRS. We repeated the search
for Forms 27 corresponding to all 4,419 patents in our dataset in August 2016
and obtained a total of 4,935 Forms 27 corresponding to a total of 3,126
patents (an increase of 1,127 patents over the initial search).
All Forms 27 that we
accessed were downloaded as PDF files or original image files and manually
entered into a text-searchable spreadsheet maintained at CIS.[141] All information from the Forms 27 was
transcribed into the spreadsheet, including all textual descriptions of patent
working and licensing. The results were then analyzed as described in Part
III.A below.
C. Limitations
The present study
was limited by the technical capabilities of the IPO’s online Form 27
repository.[142] As described above, we found significant
gaps in posted Forms 27 in our initial search, and it took a formal RTI
application to spur the IPO to upload additional forms. Yet, we still identified
1,400 fewer Forms 27 than issued patents in the mobile devices category. The
degree to which these missing forms arise from abandoned or expired patents, or
additional failures of the IPO to upload filed forms, is unclear. Other than
the IPO web site, there is no practical way to identify or access Forms 27
filed with the IPO. Technical issues with the InPASS and IPAIRS databases were
constant challenges during this study. The databases were frequently
unavailable, produced conflicting results, and were subject to numerous runtime
errors and failures.
Despite these
technical challenges, we believe that we have identified a large segment of
filed Forms 27 covering Indian patents held by all major patent holders in the
mobile device sector. We hope that this study will further encourage the IPO to
improve the regularity and reliability of its Form 27 database.
III. Findings
In this Section, we
describe the findings of our empirical collection analysis of Forms 27
pertaining to Indian patents in the mobile device sector.
A. Aggregated Data ñ Forms Found and Missing
As
noted above, we used a dataset comprising 4,419 Indian patents in the mobile
device sector issued as of February 2015. Of these, at least 107 patents were
likely expired prior to the date on which a Form 27 would have been filed,[143]
leaving 4,312 patents for which at least one Form 27 could have been
filed.
We were able to
identify and obtain a total of 4,916 valid Forms 27[144] which corresponded to 3,126 of these
patents, leaving 1,186 Indian patents for which a Form 27 could have been
filed, but was not found. This total represents 27.5% of the patents for which
at least one Form 27 could have been filed: a significant portion of the total
number of patents in the field, and within the general range of missing Forms
identified by both the Controller and Basheer (2015).
Based on the year of
grant of each of the 4,312 patents identified in the mobile device sector as to
which a Form 27 could have been filed, we determined that a total of 24,528 Forms
27 should have been filed with respect to these patents.[145] This figure represents the sum of total
Forms 27 that could have been filed for each such patent, which ranges from a
low of one to a high of eight Forms 27 per patent. In our sample, no single
patent was associated with more than five Forms 27. As noted above, we obtained
a total of 4,935 Forms 27 filed with respect to 3,126 patents, representing
only 20.1% of the total Forms 27 that should have been filed and made available
with respect to the 4,312 patents studied. Figure 1 below compares the number
of Forms 27 filed in each year since 2009 with the number of Forms 27 that
should have been filed each year based on the number of mobile device patents
in force from year to year.
Figure 1
Actual vs. Required Form 27 Filings, by year
(based on number of mobile device patents in
force)
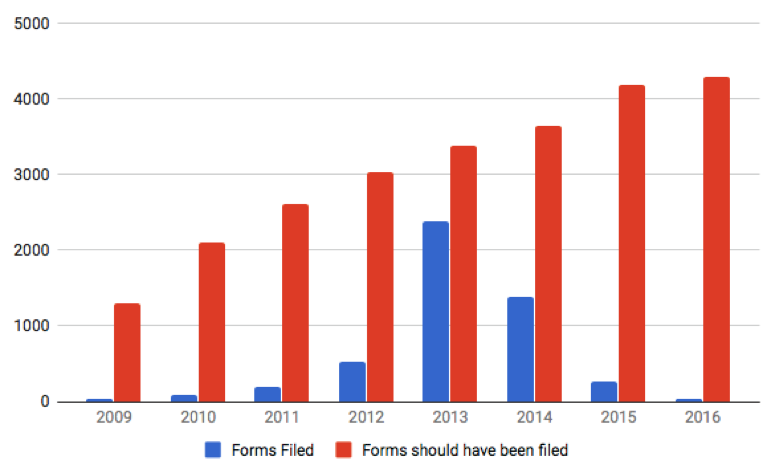
As shown in Figure
1, Form 27 filings have fallen well below the required number every year. In
2009, the first year in which Forms 27 were filed in any numbers, only 36 Forms
were filed, representing only 2.8% of the 1,302 Forms that should have been
filed based on the number of mobile device patents in force that year. By 2013,
the number of Forms filed rose to 2,389, representing 70.7% of the 3,379 Forms
that should have been filed. This ratio declined again in 2014 to 1,392 Forms
out of a total of 3,639 (38.3%). Data for 2015 and 2016 are likely incomplete
given the February 2015 cutoff for patents in our study. We also expect that
many of the 1,186 “missing” Forms 27 were filed more recently and have not yet
been uploaded by the IPO in a searchable format.
One possible
explanation for the beginning of filings in 2009 and the significant jump in
filings in 2013 may be the Controller’s public notifications of the need to
file Forms 27 in 2009 and 2013.[146]
Figure 2 below illustrates the number of
issued patents in the mobile device
sector for which Forms 27 were found and missing, categorized by patent holder
(assignee). Complete data is contained in the Appendix, Table A1.
Figure 2
Forms 27 (Identified and Missing) Per
Assignee
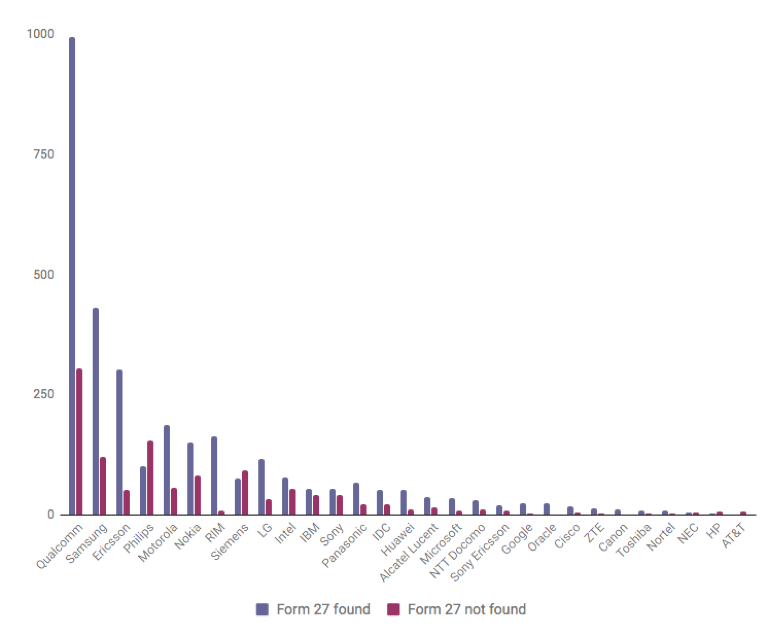
As shown in Figure
2, missing Forms 27 were distributed among most holders of Indian patents in
the mobile device sector. Of the 40 firms identified as holding issued mobile
device patents, Forms were missing for 37 of these (92.5%). In most cases, more
Forms 27 were found than missing. In a few cases, however (most notably
Philips), more Forms 27 were missing than found. In the case of four large
patent holders (Qualcomm, Siemens, Philips and Samsung), more than 100 Forms 27
were missing. Forms 27 were missing for patents with issuance dates ranging
from 2004 to 2015.[147]
There are several
possible reasons that Forms 27 may not have been identified for all issued
Indian patents. One possibility, is non-compliance by the patent holder. This
is likely the case with respect to the early years (2009-2010), when filing
requirements were not yet normalized. However, in more recent years, the
following factors suggest that patent holder non-compliance is not a significant cause of missing Forms
27 in the IPO database: (1) Forms 27 were missing for nearly all patent holders
across the board, (2) large patent holders filed hundreds of Forms 27 and were
clearly aware of their filing requirements, (3) the incremental cost of filing
Forms 27 is minimal, and (4) in most cases, large patent holders simply copy
text from one form to another (not in itself ideal, see below), requiring
little incremental effort to file additional forms. Rather, given our
experience with IPO during this study (see Methodology, above), we expect that
the missing forms are due largely to the IPO’s failure to upload Forms 27 to
its web site in a timely and reliable manner, and the dropping of Forms 27 once
uploaded.
B. Working Status
As noted above, we
reviewed 4,935 Forms 27 filed with respect to 3,126 patents in the mobile
device sector. Figure 3 below illustrates the number of patents for which Forms
27 were filed and which the assignee designated that the patent was worked
versus not worked (or, in a few cases, made no indication of working status).[148]
Figure 3
Working Status, by Assignee
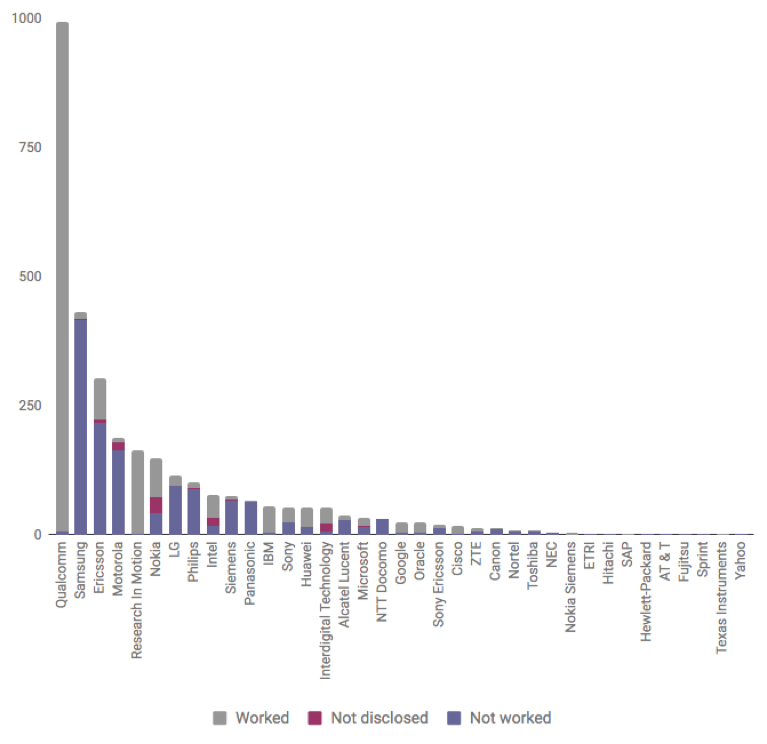
These results
suggest that different patentees have developed significantly different
strategies regarding their Form 27 filings. For example, Qualcomm, the largest
holder of patents in the mobile device sector (1,298 patents, 993 of which have
associated Forms 27), represents that nearly all of its patents (986, 99.3%)
are being worked. Samsung, on the other hand, holds the second-highest number
of patents (551 patents, 430 of which have associated Forms 27). Yet Samsung
claims that it is working only 12 of its patents (2.3%). Clearly, these two
patentees are employing different strategies regarding the declaration of
working. A glance at Figure 3 suggests that some patentees such as RIM (now
renamed Blackberry) follow Qualcomm’s approach of declaring most patents to be
worked, while others (Ericsson, LG, Motorola, Panasonic, Philips, Siemens)
follow Samsung’s approach and declare most patents not to be worked.
Of course, one might
reason that there may be some difference between the patents themselves, and
that the patentees’ declarations may simply reflect the fact that some firms’
patents are used more pervasively in India. This conjecture, however, is
unlikely. Most of the patentees studied are large multinationals whose patents
cover the same products. Many of these patents are declared as essential to the
same technical standards. Moreover, given the generally ambiguous evidence
proffered by patentees supporting their designated working status (see Part
III.C, below), we doubt there are substantial enough differences among the
patentees’ portfolios to account for the significant divide in declarations of
working status.
C. Descriptive Responses
As noted above,[149] Form 27 requires the patentee to disclose
whether or not a patent is being worked in India. If so, the patentee must
disclose the number and amount of revenue attributable to products covered by
the patent that are manufactured in India and are imported from other
countries. If the patent is not being
worked, the patentee must explain why and describe what steps are being taken
to work the invention. In both cases, the patentee must also identify licenses
and sublicenses granted and state how it is meeting public demand for products
at a reasonable price.
As first observed by
Basheer, there is widespread non-compliance with these reporting and disclosure
requirements.[150] We largely confirm this result. Below is a
summary of our findings with respect to the descriptive responses for the 4,935
Forms 27 that we reviewed.
1. Working Status Not Disclosed
For a surprising
number of Forms 27 (95 or 3%), the working status of the relevant patent was
not designated (i.e., neither the box for “worked” nor “not worked” was checked
by the patentee). Table 1 below shows the patentees that filed Forms 27 in this
manner.
Table 1
Forms 27 Failing to Disclose Working Status
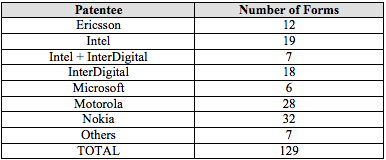
Clearly, these
sophisticated multinational firms understood the filing requirements for Form
27 and, in most cases, filed additional Forms 27 that did indicate whether the
relevant patent was or was not being worked. Thus, the principal reason for
filing a Form 27 without designating its working status appears to be the
patentee’s uncertainty regarding the patent’s working status in India.
Illustrating this
point, Motorola declares in several of its Forms of this nature that “[i]t is
not possible to determine accurately whether the patented invention has been
worked in India or not, due to the nature of the invention.”[151] While Motorola fails to explain how “the
nature of the invention” makes it impossible to determine whether or not the
patent is being worked, it uses this litany in most of its Forms 27 that fail
to disclose working status. Ericsson adopts a slightly different approach,
stating that while it is actively seeking opportunities to work the patent,
there may have been some uses of the patented technology.[152] Thus, again, it is uncertain whether the
patent is being worked or not. Presumably, these patentees felt that it was
preferable to file an incomplete, rather than incorrect, Form 27.
Interestingly, most
patentees never revised their working non-designations over the years. Thus, if
a patent was not designated as worked or not worked in the first year a Form 27
was filed, subsequent filings for that patent typically duplicated the language
of prior years’ filings. One exception appears to be Google, which acquired
Motorola’s patent portfolio in 2012. For Indian Patent No. 243210 issuing in
2010, Motorola filed Forms 27 in 2010 and 2011 without indicating whether or
not the patent was worked. However, in 2013, Google/Motorola filed a Form 27
for the same patent indicating that it was not
worked.
Google has elected
to opt for non-working when it is uncertain of the working status of a patent.
For example, the following qualified language is used in several Forms in which
Google indicates that a patent is not being worked:
Based on a reasonable
investigation, it is Google’s belief that the patent has not been worked in
India. The uncertainty arises because Google’s products and services are
covered by numerous patents belonging to Google’s very large worldwide patent
portfolio, and Google does not routinely keep track of which individual patent
is being employed in Google’s products and services. The present statement is
being filed on the basis of Google’s current estimation, but Google requests
opportunities to revise the statement, should it transpire at a later date that
the patent is being worked contrary to their present belief.[153]
2. Patents Not Worked
We examined a total
of 2,380 Forms 27 that indicated the relevant patents were not being worked. If
a patent is specified as not being worked, the patentee must disclose the
reasons for the failure to work the patent, and describe what steps are being
taken to work the invention.
In a small number of
cases, the patentee offered some plausible explanation for non-working of the
patent. The most common of these, claimed by in Ericsson in thirty-six Forms
27, was that the underlying technology was still under development,[154] making working impossible, at least until
that development was completed. In a handful of other Forms 27 (6), Ericsson
and Nokia have claimed that a patent was not being worked because it covered a
technology awaiting approval or endorsement by a standards body.[155] In the vast majority of cases, however, no
explanation is offered as to why a particular patent is not being worked.
With respect to
disclosure of the patentees’ plans for working a non-worked patent, most simply
include stock language stating that they are “actively seeking” or “on the
lookout for” commercial working opportunities in the future.[156] Alcatel-Lucent adopted an even more passive
and non-specific stance toward its plans to work patents, stating in numerous
Forms 27 (applicable to 29 patents) that “as and when there is a specific
requirement, the patent will be worked.”[157]
3. Varied Interpretations of Working
We reviewed 2,425
Forms 27 that listed the subject patent as being worked. In such cases, the
patentee must disclose the number and amount of revenue attributable to
products covered by the patent, whether manufactured in India or imported from
other countries. A tiny percentage of the Forms 27 that we reviewed provided
this information in the form requested. As we discuss in our conclusions,
below, it is likely that the format of the required response is simply
unsuitable for complex products such as mobile devices. Below we summarize and
classify the types of responses that patentees offered regarding the working of
their patents.
a. Specific Information ñ Very few Forms 27 actually provide the
specific product volume and value information required by the Form. The only
patentee that provided the specific information required by Form 27 was
Panasonic, which, with respect to the only two patents that it claimed to work
(of a total of 66 Indian patents as to which a Form 27 was found), listed
specific product volumes and values.[158]
Other patentees
disclosed specifics regarding the technical details of their worked patents,
but declined to provide product volume and value information. For example,
Ericsson discloses: “the stated patent covers a specific detail of data
transmission to a mobile in a GSM or WCDMA mobile network where said
transmission of data is not performed if the mobile has not enough battery
capacity left for the transfer.”[159] Ericsson goes on, however, to explain that
because this patented technology is intended to be used in conjunction with
other patented technologies, it is not possible to provide the financial value
of the worked patent “in isolation.”[160] Oracle also adopts this approach of offering
specific product information, while declining to estimate associated sales
volume or revenue.[161]
b. Relevance to a Standard ñ In several cases, a patentee describes its
patented invention by reference to an industry standard. For example,
Nokia-Siemens utilize the following description for one patent that is
allegedly worked: “Invention relevant for IEEE 802.16-2009 and IEEE 802.16-2011
standard.”[162] While the patentee offers no additional
information regarding the working of the patent, the desired implication,
presumably, is that the patent covers an aspect of the standard, and if the
standard is implemented in products sold in India (as it likely is), then the
patent is thereby worked.
Some patentees offer
less specific information regarding the standards that their patents cover. For
example, Ericsson states in one Form that “This patent is essential for a 3rd
Generation Partnership Project (3GPP) standard and Ericsson is also, subject to
reciprocity, committed to make its standard essential patents available through
licensing on fair, reasonable and Non-discriminatory (FRAND) terms.”[163] In this formulation, the patentee appears
both to be implying working of the patent by virtue of the implicit inclusion
of the standard in Indian products, and also to be making known its willingness
to enter into licenses in the future on FRAND terms. This future-looking
perspective, however, is not responsive to the information called for by Form
27 for patents that are allegedly being worked, and implies that the patent is
not, in fact, being worked yet in India.
c. Indian Licensees ñ Some licensees, Qualcomm in particular,
disclose that they have licensed their patents to Indian firms. These licenses
are disclosed in Qualcomm’s Forms 27 for various patents.[164] However, it is not clear what manufacturing
or other activity is carried out by these Indian licensees. Ericsson, which has
been engaged in litigation with numerous Indian and Chinese vendors of mobile
devices in India, reports that it is receiving royalties from at least two of
these entities under court order, though it stops short of stating that these
entities are licensed under Ericsson’s patents.[165]
d. Worldwide Licensees ñ In addition to Indian licensees, Qualcomm
discloses that, as of 2014, it had granted worldwide CDMA-related patent
licenses to more than 225 licensees around the world, and that CDMA-based
devices were imported into India from “countries such as Canada, China,
Finland, Germany, Italy, Japan, Korea, Switzerland, Taiwan, and the United
States.”[166] While Qualcomm is not specific regarding the
linkage, if any, between its worldwide licensees and mobile devices sold in
India, it reports that more than 37.7 million CDMA-based mobile devices were
sold in India in 2014 at an average price of USD $161.94.[167] And though not express, the implication of
these data is that all CDMA-based mobile devices sold in India somehow utilize
Qualcomm’s patented technology.
The granting of
worldwide licenses raises an interesting question regarding local working of
patents. As Ericsson (which claims to have executed more than 100 patent
licensing agreements) explains, its global licensees are, by definition,
licensed in every country, including India. Because their global license
agreements “are operational in India”, the licensees are theoretically
authorized to work Ericsson’s patents in India. But it is not clear that this
means that the patents are actually
being worked in India. Simply granting a worldwide patent license does not mean
that the licensed patent is being worked, just as the issuance of a patent in a
country does not mean that the patent is being worked in that country.
e. Too Big to Know ñ Some patentees claim that they or their
patent portfolios are simply too vast to determine how particular patents are
being worked in India, or the number or value of patented products sold in
India. Nokia, for example, uses the following language in 82 separate Form 27
filings: “Nokia’s products and services are typically covered by tens or
hundreds of the nearly 10,000 patents in Nokia’s worldwide portfolio. Nokia
does not keep records of which individual patents are being employed in each of
Nokia’s products or services, and is therefore unable to report the quantum and
value of its products or services which employ the patented invention.”[168]
In a similar vein,
Ericsson notes that its patented technologies are intended to be used in
combination with a large number of other technologies patented by Ericsson and
others. Accordingly, “it is close to impossible to prove an indication of
specific or even close to accurate financial value of the said patent in
isolationÖ”[169] This said, Ericsson goes on to disclose its
total product sales in India (3.09 billion SEK in 2013) and also notes that it
earns revenue from licensing its patents (without disclosing financial data).[170]
f. On the Lookout ñ Curiously, some patentees that claim to be
working their patents use the same language regarding their search for working
opportunities as they and others use with respect to non-worked patents. For
example, Ericsson makes this statement regarding some of the patents that it is
allegedly working in India: “The patentee is in the lookout for appropriate
working opportunities in a large scale although there may have been some use of
the patented technology in conjunction with other patented technologies.”[171] This language is uncertain and does not seem
to support a claim that, to the patentee’s knowledge, the patent is actually
being worked. At best, it expresses optimism toward the possibility of finding
an opportunity to work the patent in the future.
g. Information Provided Upon Request ñ Some patentees decline to provide any
information about the working of their patents in Forms 27, but offer to
provide this information if requested (presumably by a governmental authority).[172] Some patentees further explain their
hesitation to provide this information in Form 27 on the basis that the
information is confidential, but commit to provide it if requested.[173]
h. Corporate PR ñ Some patentees, in addition to, or in lieu
of, providing information about their patents, offer general corporate
information of a kind that would often be found in corporate press releases and
annual reports. For example, Research in Motion offers this glowing corporate
report in lieu of any information about its allegedly worked patents:
Patentee is a
leading designer, manufacturer and marketer of innovative wireless solutions
for the worldwide mobile communications market. Through the development of integrated
hardware, software and services that support multiple wireless network
standards, the patentee provides platforms and solutions for seamless access to
time-sensitive information including email, phone, SMS messaging, internet and
intranet-based applications. Patentee’s technology also enables a broad array
of third party developers and manufacturers to enhance their products and
services with wireless connectivity. Patentee’s portfolio of award-winning
products, services and embedded technologies are used by thousands of
organizations around the world (including in India) and include the Blackberry
wireless platform, the RIM Wireless Handheld product line, software development
tools, radio-modems and software/hardware licensing agreements.[174]
RIM then goes on to
explain that it has so many patents that identifying how the instant patent is
worked in India is impossible (see “Too Big to Know” above).
Ericsson likewise
offers a bit of self-serving corporate history in twenty-eight different Forms
27 in which it states:
Ericsson’s history
in India goes back 112 years during which period Ericsson has contributed
immensely to the telecommunication field in India. Ericsson provides, maintains
and services network for several major government and private operators in
India. At present, Ericsson has more than 20,000 employees across 25 offices in
India. Further, Ericsson has established manufacturing units, global service
organization and R&D facilities in India…[175]
i. Just Don’t Know ñ Some patentees simply assert that they are
unable to determine information regarding working of their patents, without any
explanation why. Alcatel-Lucent, for example, offers the following unsatisfying
disclosure with respect to the eight patents that it claims to be working in
India: “The patentee is unable to particularly determine and provide with
reasonable accuracy the quantum and value of the patented invention worked in
India, including its manufacture and import from other countries during the
year 2014.”[176]
j. No Description ñ Some patentees simply omit to provide any
information whatsoever regarding the working of their patents, even when
patents are allegedly worked.[177]
4. Changes in Status
While some of the
“boilerplate” responses provided by patentees in their filed Forms 27 might
suggest that patentees give little thought to the content of Form 27 filings,
we identified a small but non-trivial number of patents (4.1%) as to which the
patentee changed the working status, either from worked to not worked, or vice
versa. Overall, we identified 128 instances in which the working status of a
patent was changed from one year to the next. Of these, 51 went from worked to
not worked, and 77 went from not worked to worked. Such changes suggest that
patentees give at least some thought to the manner in which they work their
patents, and seek to correct inaccurate disclosures, though these observed
variances could also be attributed to changes in law firm, changes in
interpretation of filing requirements or mere clerical errors and
inconsistencies in filings from year to year.
In 17 cases, the
status of the same patent changed twice
over the course of three or more Forms 27. Almost all of these three-stage
“flip-flops” moved from worked to not worked to worked, with the aberrant ‘not worked’
year occurring in 2013. In fact, 2013 seems to have been a popular year for
changes in working status, whether because of heightened awareness, and
therefore greater scrutiny of Form 27 filings due to the Controller General’s
public notice of that year, or changes in interpretation of filing requirements
occasioned by a widely-attended seminar or article. But whatever the cause, it seems highly
unlikely that, over the course of three years, a single patent could go from
being worked in India, to not being worked, to being worked again. As a result,
we attribute these flip-flop changes primarily to filing errors and
inconsistencies rather than genuine attempts to correct inaccurate disclosures.
Corresponding to
changes in working status, patentees often changed the textual descriptions of
working or non-working contained in their Forms 27. These changes usually
involved adding stock language regarding working or non-working to a Form 27
that previously contained no descriptive information. However, in some cases
the patentee’s descriptive text bears little relation to the purported working
status of the patent. For example, as illustrated in Table 2 below, a single
patentee’s disclosures with respect to two different patents across three
filings employ the same textual descriptions but for different working status.
Table 2
Comparison of Working Status Descriptions
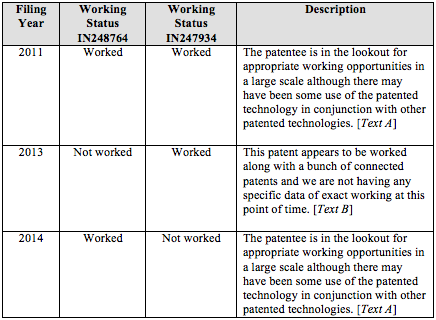
As illustrated by
Table 2, the patentee’s working description (Text A) is identical in 2011 and
2014 for both patents, though in 2014 one patent is allegedly worked and the
other is not. Likewise, in 2013, one patent is worked and the other is not, yet
the textual description for both is identical (Text B). Putting aside, for a
moment, the fact that neither Text A not Text B is particularly responsive to
the information requirements of Form 27, it is puzzling why the patentee would
use the same stock language to describe both working and non-working of its
patents. The only consistency that emerges from this example is across filing
years, suggesting, perhaps, that the textual descriptions used in these forms
was more dependent on the person or firm making the filing in a particular year
than the alleged working status of the patents in question.
IV. Discussion and Analysis
Professor Basheer
charges that significant numbers of Forms 27 are “grossly incomplete,
incomprehensible or inaccurate,” and has sued the Indian Patent Office to
compel it to improve its monitoring and enforcement of Form 27 filings.[178] Our results confirm that there are overall
weaknesses in the Indian Form 27 system, several of which reveal deeper
problems with the implementation of India’s patent working requirement.
A. Process Weaknesses
Though filings in
support of India’s patent working obligation have been required since 1972, and
Form 27 has been on the books since 2003, meaningful filings of Form 27 did not
begin until the Controller’s first public notice on this topic in 2009. In the
following eight years, Form 27 filings have increased, but are still well below
required levels (see Part III.A, above). Even at their peak in 2013, we located
only 70.7% of required Forms 27 in the mobile device sector, a sector
characterized by sophisticated firms that are advised by counsel. Filing ratios
were significantly lower in every other year.
There are several
possible reasons for these discrepancies. First are possible issues with the
IPO’s electronic access to records. As noted in Part II, we experienced
significant difficulties obtaining Forms 27 through the IPO’s web site. It was
only after two RTI requests that significant numbers of Forms 27 were made accessible
online. It is possible that the IPO has additional Forms 27 in its files that
have not been made accessible electronically. For a system the purpose of which
is to make information about non-worked patents available to the public, such
lapses are inexcusable, particularly given that India’s current working
requirement is nearing its 50th anniversary. Accordingly, we expect
that improvements to the IPO’s electronic filing and access systems may improve
the profile of Form 27 filing compliance.
B. Non-Enforcement and Non-Compliance
As noted above, we
expect that some portion of the apparent non-compliance with India’s Form 27
requirement is attributable to the inaccessibility of properly filed Forms 27.
However, it is also likely that some portion of the deficit in available Forms
27 is due to actual non-compliance by patentees. Though there are stiff
penalties on the books for failing to comply with Form 27 filing requirements,
including fines and imprisonment,[179] we are unaware of any enforcement action by
the IPO or any other Indian governmental authority regarding such
non-compliance.[180]
Given that records
of all issued Indian patents are available online, and that all filed Forms 27
should also be available online, it would not seem particularly difficult for
the IPO to implement an automatic monitoring and alert system warning patentees
that they have not filed required Forms 27. Such a system would likely increase
compliance substantially. However, we find no evidence that the IPO monitors or
otherwise keeps track of Form 27 filings or seeks to contact patentees who fail
to meet their filing requirements. As a result, it is not surprising that
non-compliance is widespread.
C. Uncertainty Surrounding Working and Complex Products
When Forms 27 are
filed, many of them lack any meaningful detail regarding the manner in which
patents are worked or the reasons that they are not worked. While the
descriptive requirements of Form 27 are quite clear, even the largest and most
sophisticated patentees seemingly struggle with determining whether or not a
patent is actually worked in India and, if so, how to quantify its working in
the manner required by the Form. There are several reasons that this degree of
uncertainty exists. First, India has no clear statutory, regulatory or judicial
guidelines for interpreting its working requirement. As the court noted in Natco, the working determination must be
made on a case by case basis, with attention to the specific details of the
patent in question.[181] This open-ended standard offers little
guidance to firms regarding the degree to which importation or licensing may
qualify as working a patent, or even what degree of assembly, packaging or
distribution within India will so qualify.
Additionally, some
patentees have taken the position in their Forms 27 that merely licensing a
patent to an Indian firm qualifies as working the patent in India.[182] Some have even gone so far as to take the
position that granting a worldwide
patent license qualifies as working the licensed patent in India, given that
India is part of the world.[183] These conclusions seem stretched, but they
have not, to our knowledge, ever been challenged by the IPO or any private
party.
What’s more, several
patentees take the position that it is impossible to determine the value
attributable to a single patent that covers only one element of a complex
standard or product (“too big to know”).[184] While these patentees may disclose the size
of their large patent portfolios or total Indian product revenues, these
figures do not provide the information required by Form 27 relative to the
individual patent that is claimed to be worked.
Given the degree of
uncertainty surrounding the Indian working requirement and how it is satisfied,
it is not surprising that the disclosures contained in most Forms 27 are
meaningless boilerplate that convey little or no useful information about the
relevant patents or products. Moreover, it is questionable whether it is even possible for a willing patentee to
provide the product and revenue information currently required by Form 27 for
complex, multi-patent products such a mobile devices.[185] It may be time for the IPO to revisit the
information requirements of Form 27, which were seemingly developed with
products covered by one or a handful of patents in mind, to more suitable
address complex electronic and communications products that may be covered by
hundreds or thousands of patents each.
D. Strategic Behavior
In an environment of
extreme uncertainty and low enforcement, it is not surprising that patentees
have developed self-serving strategies to achieve their internal goals while
arguably complying with the requirements of Form 27. Evidence of strategic
behavior can be seen clearly in the divide between those patentees that claim
that they are working most of their patents and those that claim that they are
not.[186] We can assume that there are not significant
differences in the portfolio make-up among these different patentees, so the
large difference between their ratios of worked and non-worked patents must be
attributable primarily to decisions made to further corporate interests.
For example, it is
possible that those patentees claiming significant working of their patents do
so in order to avoid requests for compulsory licenses against their patents.
Such patentees may wish to exploit the Indian market themselves, or license
others to do so on terms of their choosing, so may seek to avoid compulsory
licensing on terms dictated by the government. Those patentees claiming
significant non-working, on the other hand, may actively be seeking applications for compulsory
licensing. Why? Perhaps because these patentees do not plan to sell products in
India and see little prospect of entering into commercial license agreements
with Indian producers. Thus, their greatest prospect of any financial return on
their patents may be a compulsory license. As unlikely as it sounds, they may
be using Form 27 as a legally-sanctioned “To Let” sign for otherwise
unprofitable patents.[187]
Whatever the
underlying reasons are for patentee strategic decisions in the filing of Forms
27, IPO owes the public greater clarity regarding the formal requirements for
working patents in India. It is only when disclosures are made in a consistent
and understandable format that the public will acquire the knowledge about
patent working that the Act intends for them to receive.
E. Opportunities for Further Study
This is the first
comprehensive and systematic study of reporting compliance with India’s patent
working requirements. It covers only one industry sector: mobile devices.
Expanding this study to additional industry sectors, particularly
pharmaceuticals and biomedical products, would likely yield additional
insights.
It would also be
informative to revisit the instant set of patents in a few years time to
determine whether increased IPO access to electronic records may alter the
somewhat poor compliance landscape revealed by this study. That is, if a
significant number of Forms 27 that have been filed are simply unavailable
through the IPO’s web site, then hopefully continued information technology
improvements at the IPO will improve availability in years to come.
Conclusion
India’s annual Form
27 filing requirement is intended to provide the public with information
regarding the working of patents in India so as to enable informed requests to
be made for compulsory licenses of non-worked patents. While such a goal is
laudable, it is not clear that this system is currently achieving the desired
results.
In the first
systematic study of all Forms 27 filed with respect to a key industry sector ñ
mobile devices ñ we found significant under-reporting of patent working, likely
due to some combination of systemic deficiencies and non-compliance by
patentees. Thus, from 2009 to 2016, we could identify and access only 20.1% of
Forms 27 that should have been filed in this sector, corresponding to 72.5% of
all mobile device patents for which Forms 27 should have been filed. Forms 27
were missing for almost all patentees, suggesting that defects in the Indian
Patent Office’s online access system may play a role in the unavailability of
some forms.
But even among Forms
27 that were accessible, almost none contained useful information regarding the
working of the subject patents or fully complying with the informational
requirements of the Form and the Indian Patent Rules. Patentees adopted
drastically different positions regarding the definition of patent working,
some arguing that importation of products into India or licensing of Indian
suppliers constituted working, while others even went so far as to argue that
the granting of a worldwide license to a non-Indian firm constituted working in
India. Several significant patentees claimed that they or their patent
portfolios were simply too large to enable the provision of information
relating to individual patents, and instead provided gross revenue and product
sale figures, together with historical anecdotes about their long histories in
India. And many patentees simply omitted required descriptive information from
their Forms without explanation.
The Indian
government has made little or no effort to monitor or police compliance with
Form 27 filings, likely encouraging non-compliance. Moreover, some of the
complaints raised by patentees and industry observers regarding the structure
of the Form 27 requirement itself have merit. Namely, patents covering complex,
multi-component products that embody dozens of technical standards and
thousands of patents are not necessarily amenable to the individual-level data
requested by Form 27. We hope that this study will contribute to the ongoing conversation
in India regarding the most appropriate means for collecting and disseminating
information regarding the working of patents.
APPENDIX
TABLE A1
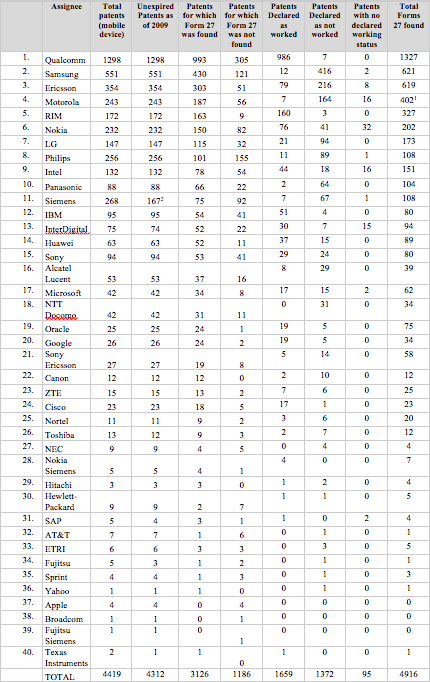
[1] Natco Pharma Ltd. v. Bayer Corp., (2011) I.P.O. Order No. 1, at 6
(India).
[2] See
id.
[3] The Natco case is one in a long line of
cases in the ongoing “access to medicines” dispute, in which developing
countries seek compulsory licenses for local use of lifesaving drugs that are
patented by western pharmaceutical firms. See,
e.g., Srividhya Ragavan, Patent and
Trade Disparities in Developing Countries (2012); Charles R. McManis and
Jorge L. Contreras, Compulsory Licensing
of Intellectual Property: A Viable Policy Lever for Promoting Access to
Critical Technologies?, in TRIPS and Developing Countries ñ Towards a New
IP World Order? (Gustavo Ghidini, Rudolph J.R. Peritz & Marco
Ricolfi, eds. 2014); Jerome H. Reichman, Comment: Compulsory Licensing of Patented Pharmaceutical Inventions:
Evaluating the Options, 37 J. L. Med.
& Ethics 247, 250 (2009).
[5] See
Patents Act, No. 39 of 1970, India Code
(1970), ch. XVI, § 84(1).
[6] See Rochelle
Dreyfuss & Susy Frankel, From
Incentive to Commodity to Asset: How International Law Is Reconceptualizing
Intellectual Property, 36 Mich. J.
Int’l L. 557, 576 (2015); See also
Feroz Ali, Picket Patents: Non-Working as
an IP Abuse, at *5, https://papers.ssrn.com/sol3/papers.cfm?abstract_id=2732521 (last visited Feb. 6, 2017); see also Bryan Mercurio & Mitali
Tyagi, Treaty Interpretation in WTO
Dispute Settlement: The Outstanding Question of the Legality of Local Working
Requirements, 19 Minn. J. Int’l L. 275,
281 (2010).
[7] Marketa Trimble, Patent Working Requirements: Historical and Comparative Perspectives,
6 U.C. Iʀᴠɪɴᴇ L. Rᴇᴠ. 483, 500-501
(2016).
[8] Id.
at 495.
[9] Jorge L. Contreras & Rohini Lakshané, Patents and Mobile Devices in India: An
Empirical Survey, 50 Vand. Transnat’l
L.J. 1 (2017). The data set used in the foregoing study can be found at https://cis-india.org/a2k/blogs/dataset-patent-landscape-of-mobile-device-technologies-in-india.
[10] Trimble, supra
note 7, at 488. In England, royal patents were
granted to foreigners who would teach their art to the local population. Id.
at 488, 497. Venice provided monopoly rights and tax holidays for foreign
inventors to immigrate and improve local industrialization. Ragavan, supra note 3, at 3.
[11] See Ragavan, supra note 3, at 3; see
also G.B. Reddy & Harunrashid A. Kadri, Local Working of Patents ñ Law and Implementation in India, 18 J. Intell. Prop. Rights 15, 15 (2013).
[15] See
generally Paul Champ & Amir Attaran, Patent Rights and Local Working Under the WTO TRIPS Agreement: An
Analysis of the U.S.-Brazil Patent Dispute, 27
Yale J. Int’l L. 365, 371 (2002).
[16] Trimble, supra
note 7, at 498 (“In the United Kingdom in the 18th
century ‘the requirement of compulsory working dropped into desuetude and its
place was taken for all practical purposes, in particular in the practice of
the law courts, by [the full disclosure] requirement’”) (alterations in
original) (internal citations omitted).
[17] Paris Convention for the Protection of
Industrial Property, World Intellectual Property Organization, art. 5(A)(1),
March 20, 1883.
[18] See Reddy
& Kadri, supra note 11, at 17; see
also Champ & Attaran, supra
note 15, at 371; Trimble, supra note 7, at 493ñ94.
[19] Hague Revision to Paris Convention for the
Protection of Industrial Property, World Intellectual Property Organization,
art. (5)(A)(2), November 6, 1925.
[20] See Champ
& Attaran, supra note 15, at 372; see
also Trimble, supra note 7, at *490-94 (tracing history of remedies for
failure to meet working requirements, including forfeiture).
[21] London Revision to Paris Convention for the
Protection of Industrial Property, World Intellectual Property Organization,
art. 5(A)(4), June 2, 1934; See
Trimble, supra note 7, at 494.
[22] Stockholm Revision to Paris Convention for
the Protection of Industrial Property, World Intellectual Property Organization,
art. 5(A)(2), July 14, 1967.
[23] See Trimble,
supra note 7, at 494-95; see also Janice M. Mueller, The
Tiger Awakens: The Tumultuous Transformation of India’s Patent System and the
Rise of Indian Pharmaceutical Innovation, 68 U. Pitt. L. Rev. 491, 517-18 (2007)..
[25] See Ragavan, supra note 3, at 65-66. See
generally TRIPS: Agreement on Trade-Related Aspects of Intellectual
Property Rights, Apr. 15, 1994, Marrakesh Agreement Establishing the World
Trade Organization, Annex 1c, 1869 U.N.T.S. 299, 33 I.L.M. 1197 (1994), reprinted in World Trade Organization, The Results of the Uruguay Round of
Multilateral Trade Negotiations 365 (1995) [hereinafter “TRIPS
Agreement”].
[26] Additionally, those countries that were not
members of the Paris Union but are members of the WTO are therefore obligated
to comply with the Paris Convention and its revisions under Article 2.2 of the
TRIPS Agreement.
[28] TRIPS Agreement, supra note 25, art. 30-31; see also Ragavan, supra note 3; McManis and Contreras, supra note 3.
[29] See
generally Trimble, supra note 7, at 496; Shamnad Basheer, Making Patents Work: Of IP Duties and
Deficient Disclosures, 7 Queen Mary
J. Intell. Prop. 3, 16-17 (2017).
[30] Request for Consultations by the United
States, Brazil ñ Measures Affecting
Patent Protection, WTO Doc. WT/DS199/1 (June 8, 2000); see also Reddy & Kadri, supra
note 11, at 17;
Trimble, supra note 7, at 496-497.
[32] Article 28(1) of the TRIPS Agreement defines
the rights that may be conferred on patent owners.
[34] Id. at 381. The two patented drugs that the
Brazilian Ministry of Health threatened to grant compulsory licenses on were
efavirenz and nelfinavir. These drugs are antiretroviral drugs used to treat
AIDS. Geoff Dyer, Brazil Defiant Over
Cheap AIDS Drugs, Fin. Times,
Feb. 9, 2001, at 10.
[35] Barbara Crossette, U.S. Drops Case Over AIDS Drugs in Brazil, N.Y. Times (June 26, 2001), http://www.nytimes.com/2001/06/26/world/us-drops-case-over-aids-drugs-in-brazil.html.
[36] Kalyan C. Kankanala, Arun K. Narasani &
Vinita Radhakrishnan, Indian Patent Law & Practice 1 (2010).
[38] Shri Justice N. Rajagopala Ayyangar, Report on the Revision of the Patents Law
(September 1959) [hereinafter “Ayyangar Report”]; Ragavan, supra
note 3, at 31-33.
[39] P.
Narayanan, Patent Law 5 (4th ed. 2006).
[42] Id.
at 39-40.
[43] See
generally The Patents Act, No. 39 of 1970,
India Code (1970).
[45] The Patents Act, 1970 § 83 (emphasis added).
[46] The Indian Controller General of Patents,
Designs & Trade Marks, who will be referred to herein as the Controller for
simplicity.
[47] The Patents Act, 1970, § 84(1) (emphasis added). The
three-year time period reflected in the Act is derived from Section 5(A)(4) of
the Paris Convention (current numbering). See
supra note 22.
[48] The Patents Act, 1970 § 84(1).
[49] Id.
§ 90(c).
[50] Id.
[51] Id.
§ 89(3). While the language of Section 89 is couched in terms of the
“reasonable requirements of the public,” it is interesting to note that the
caption of the section reads “Revocation of patents by the Controller for
non-working,” thus focusing more explicitly on the working requirement.
[52] The Patents Act, 1970 § 89(1). The two-year
time period reflected in the Act is derived from Section 5(A)(3) of the Paris
Convention (current numbering). See supra
note 21 and accompanying text.
[53] See
India and the WTO, Wᴏʀʟᴅ Tʀᴀᴅᴇ Oʀɢ.,
http://www.wto.org/english/thewto_e/countries_e/india_e.htm. See generally TRIPS Agreement.
[54] India amended its 1970 Act in three
amendments, corresponding to the transition periods permitted by the TRIPS
Agreement. India played a significant role in establishing the TRIPS multi-year
transition periods. See Mueller, supra note 23, at 518. For a discussion of India’s
political and economic considerations underlying its support of compulsory
licensing under TRIPS, see Omar
Serrano & Mira Burri, Making Use of
TRIPS Flexibilities: Implementation and Diffusion of Compulsory Licensing
Regimes in Brazil and India (World Trade Inst. Working Paper No. 1 2016).
[55] The Patents (Amendment) Act, No. 38 of 2002,
India Code (2002).
[56] Id.
§ 85.
[57] Id.
§ 83(c).
[58] Id.
§ 83(d)-(f).
[59] Id. § 89.
[60] Id.
§ 84(1) (emphasis added).
[61] Id.
[62] Id.
§ 84(6).
[63] See Thomas
Cottier, Shaheeza Lalani & Michelangelo Temmerman, Use It or Lose It: Assessing the Compatibility of the Paris Convention
and TRIPS Agreement with Respect to Local Working Requirements, 17 J. Int’l Econ. L. 437, 441 (2014).
[64] See The
Patents Act, No. 39 of 1970, India Code
(1970), § 90(2) (“No license granted by the Controller shall authorise the
licensee to import the patented article or an article or substance made by a
patented process from abroad where such importation would, but for such authorisation,
constitute an infringement of the rights of the patentee.”).
[66] Natco Pharma Ltd. v. Bayer Corp., (2011)
I.P.O. Order No. 1, 5 (India).
[67] Id.
at 22.
[68] Id.
at 25 (noting that an average Indian government employee would have to work for
3.5 years to afford a single month’s dosage).
[69] Id.
at 6.
[70] Id.
at 5.
[71] Id.
[72] Id.
at 6.
[73] Id.
[74] Id. at 37.
[75] Id.
[76] Id.
at 38.
[77] Id.
at 40-41.
[78] Id.
at 43.
[79] Id.
at 45 (“I am therefore convinced that ‘worked in the territory of India’ means
‘manufactured to a reasonable extent in India.’”).
[80] Id. at
60.
[81] Natco Pharma Ltd. v. Bayer Corp., (2013)
I.P.A.B. Order No. 45 (India).
[82] Id.
[83] Id.
[84] Id.
at 43.
[85] Bayer Corp. v. Union of India, Bombay High
Ct. at 29 (Jul. 15, 2014).
[86] Id.
[87] Id.
[88] Id.
at 24.
[89] Id.
Bayer subsequently appealed to the Indian Supreme Court, which declined to hear
the case. See Samanwaya Rautray, Nexavar License Case: SC Dismisses Bayer’s
Appeal Against HC Decision, Economic
Times, Dec. 13, 2014,
[90] Harsha Rohatgi, Indian Patent Office Rejects Compulsory Licensing Application: BDR
Pharmaceuticals Pvt. Ltd. vs. Bristol Myers Squibb, Khurana & Khurana (last visited Oct.
20, 2017), http://www.khuranaandkhurana.com/2013/11/13/indian-patent-office-rejects-compulsory-licensing-application-bdr-pharmaceuticals-pvt-ltd-vs-bristol-myers-squibb/.
[91] Patralekha Chatterjee, 2013: India Battles for Right to Use Compulsory Licenses to Make
Medicines Affordable, Intellectual
Property Watch (last visited Oct. 20, 2017), https://www.ip-watch.org/2013/01/22/2013-india-battles-for-right-to-use-compulsory-licences-to-make-medicines-affordable/.
[92] See
Pankhuri Agarwal, DIPP Drags the
Dasatinib Compulsory License Drama: A Situation of ‘Extreme Urgency’?,
SpicyIP blog (Sep. 24, 2016), https://spicyip.com/2016/09/dipp-drags-the-dasatinib-compulsory-license-drama-a-situation-of-extreme-urgency.html. See,
e.g., IPO Order No. C.L.A. No.1
of 2015, In the matter of Lee Pharma Ltd v. AstraZeneca AB, dated January 19,
2016 (rejecting application due to lack of evidence presented under all three
prongs of Section 84 analysis).
[93] For example, Article 68 of Brazil’s 1996
Industrial Property Law subjects a patentee to compulsory licensing if the
patentee does not exploit “the object of the patent within the Brazilian
territory for failure to manufacture the product or failure to use a patented
process.” 68 C.P.I., Law No. 9,279 (Brazil, May 14, 1996). For additional
examples, See Cottier et al., supra note 63, at 461-71.
[94] While form submissions to show the working
of a patent are unique to India’s patent law, a submission requirement to
maintain intellectual property rights is similarly used in the United States
for trademarks. In the United States, registered trademark owners must submit a
declaration of use to avoid cancellation of the registration. See 15 U.S.C. § 1058.
[95] The Patents Act, No. 39 of 1970, India Code (1970), § 146(2).
[96] Id.
[97] The Patent Rules, Rule 131, India (2003).
[98] The Patent Rules, Rule 131, India (2003).
There is an apparent discrepancy between section 146(2) of the India Patents
Act, 1970 and Rule 131 of the Patent Rules, 2003. While section 146 suggests
that patentees should file Forms 27 every six months, Rule 131 of the Patent
Rules, 2003 requires the statements to be furnished in respect of every
calendar year.
[99] The Patents Act, No. 39 of 1970, India Code (1970), § 146(2).
[100] The public requirement refers to “the
reasonable requirements of the public with respect to the patented invention.”
The Patents (Amendment) Act, No. 38 of 2002, India
Code (2002), § 84(1)(a). In other words, if the patentee must explain
how he has or has not met his duties under section 83 and 84 of the Patents
Amendment Act of 2002.
[101] Patents Rules, Form 27, 2003.
[102] The Patents (Amendment) Act, No. 38 of 2002,
India Code (2002), § 122 provides:
“1) If any person refuses or fails to
furnish-Ö b) to the controller any information or statement which he is
required to furnish by or under section 146,
he shall be
punishable with [a] fine which may extend to twenty thousand rupees.
2) If
any person, being required to furnish any such information as is referred to in
sub-section (1), furnishes information or statement which is false, and which
he either knows or has reason to believe to be false or does not believe to be
true, he shall be punishable with imprisonment which may extend to six months,
or with fine, or with both.”
[103] Annual Report 2007-08, Office of the
Controller General of Patents, Designs, and Trade Marks including GIR and
PIS/NIIPM (IPTI), at 12; see also
Reddy & Kadri, supra note 11, at 21.
[104] Annual Report 2008-09, Office of the
Controller General of Patents, Designs, Trade Marks and Geographical
Indications, at 21; Annual Report 2007-08, Office of the Controller General of
Patents, Designs, and TradeMarks including GIR and PIS/NIIPM (IPTI), at 12; see also Reddy & Kadri, supra note 11, at 21-22.
[105] Controller Gen. of Patents, Designs and
Trade Marks, Public Notice No. CG/PG/2009/179, Dec. 24, 2009; Controller Gen.
of Patents, Designs and Trade Marks, Public Notice No. CG/Public
Notice/2013/77, Feb. 12, 2013; Controller Gen. of Patents, Designs and Trade
Marks, Public Notice No. CG/Public Notice/2015/95, 2015.
[106] The Patents Act, No. 39 of 1970, India Code (1970), § 122. (A patentee
may be imprisoned for submitting false information).
[107] Reddy & Kadri, supra note 11, at 22; see
also Shamnad Basheer v. Union of India, Writ Petition, at F (Del. 2015)
[hereinafter Basheer Writ Petition (2015)] (“[T]he Respondents authorities have
never initiated action against any of the errant patentees.”).
[108] Prashant Reddy, Patent Office Publishes All ‘Statements of Working’ ñ Finally!, Spicy IP, (June 25, 2013) https://spicyip.com/2013/06/patent-office-publishes-all-statements.html.
[109] See,
e.g., Basheer Writ Petition (2015), supra
note 107 (raising numerous deficiencies with Form
27); Shamnad Basheer & N. Sai Vinod RTI
Applications and ‘Working’ of Foreign Drugs in India, Spicy IP, at 5 (Apr., 2011) (“However,
Form 27 in its present format leaves much to be desired and we will be drafting
a more optimal Form 27 and forwarding this to the government for consideration,
so that the form can be a lot more clearer and can call for a greater range of
information.”).
[110] Letter from Philip S. Johnson, President,
Intellectual Prop. Owners Assn., to Hon. Michael Froman, U.S. Trade
Representative (Feb. 7, 2014).
[111] Id.
[112] Id.
[113] Prathiba Singh & Ashutosh Kumar, When in Rome, do as the Romans do, IP Pro Life Sciences at 16, (Mar. 10, 2013)
http://ipprolifesciences.com/ipprolifesciences/IPPro%20Life%20Sciences_issue_04.pdf.
[114] Among other things, Prof. Basheer is the
founder of the SpicyIP blog, a leading source of intellectual property news and
commentary in India. See Part III.A, infra, for a discussion of the results
of his studies of Form 27 compliance.
[117] Id.
at 1, 8.
[118] Shamnad Basheer v. Union of India, Writ
Petition No. 5590 (Del. 2015), Application Seeking Permission to Intervene in
the Above Public Interest Litigation (2016). Some of the issues raised by Mr.
Thappeta are discussed in Part IV below.
[119] Bayer Corp. v. Union of India, Writ Petition
No. 1323 of 2013, Judgment at 8ñ10 (Jul. 15, 2014).
[121] Indian Patent Office reporting year (Apr. 1
– Mar. 31).
[124] This study pre-dates the electronic
availability of Forms 27.
[126] Basheer Writ Petition (2015), supra note 107, at Annexure P-11, tbl. I. It is not clear
how the studied patents were selected. They do not represent the totality of
patents in the designated industry sectors. Likewise, it is not clear how
“publicly-funded research” is defined nor the amount of such funding behind the
selected patents.
[127] It appears that this study covered three
“reporting years” at the IPO: 2009-10, 2010-11 and 2011-12. Reporting years run
from April 1 to March 31.
[128] This figure is calculated as 1 – 263/421.
Prof. Basheer has reported this ratio as approximately 35%. Basheer, supra note 29, at 18.
[130] Id.
at 10.
[133] See
Contreras & Lakshané, supra note 9, at 27-28 (describing electronic search and
case harvesting methodology).
[134] Searches were conducted and results were
compiled by a contracted Indian service provider selected through a competitive
bid process.
[135] While InPASS and IPAIRS retrieve Form 27
submissions from the same URL, we observed that sometimes a submission that was
displayed on data base was not displayed on the other. Thus, IPAIRS was used
when Form 27 was not found for a queried patent on InPASS. InPASS has two
features: Application Status and E-Register. At times, some forms were not
available at E-Register that could be found through the Application Status
table, and vice versa. Thus, both features were used. A detailed, step-by-step
description of the search methodology used can be found at http://cis-india.org/a2k/blogs/methodology-statements-of-working-form-27-of-indian-mobile-device-patents.
[136] Ajoy Kumar, “Request for Information under
Section 6 of the Right to Information Act, 2005; regarding Form 27 Submissions
for Patents,” The Centre for Internet and Society, (June 10, 2015), https://cis-india.org/a2k/blogs/rti-app-2015.pdf/at_download/file.
[137] Boudhik Bhawan, “Supply of information
sought under RTI ñ reg,” The Centre for Internet and Society, (June 17, 2015), https://cis-india.org/a2k/blogs/rti-reply-2015.pdf/at_download/file.
[138] Ajoy Kumar, “Request for Information under
Section 6 of the Right to Information Act, 2005; regarding Form 27 Submissions
for Patents,” The Centre for Internet and Society, (Mar. 11, 2016), https://cis-india.org/a2k/blogs/rti-app-2016.pdf/at_download/file.
[139] Id.
[140] Ujjwala Haldankar, “Supply of information
sought under RTI, 2005 ñ reg,” The Centre for Internet and Society, (Apr. 4,
2016), https://cis-india.org/a2k/blogs/rti-reply-2016.pdf/at_download/file.
[141] Rohini Lakshané, Dataset for “Patent Working
Requirements and Complex Products: An Empirical Assessment of India’s Form 27
Practice and Compliance,” The Centre for Internet and Society (Aug. 17, 2017), https://cis-india.org/a2k/blogs/dataset-for-patent-working-requirements-and-complex-products-an-empirical-assessment-of-indias-form-27-practice-and-compliance.
[142] Similar deficiencies with the IPO’s online
filing facility have been noted by Basheer. See Basheer Writ Petition
(2015), supra note 107, at 17.
[143] Prior to the 2002 Amendments to the Patents
Act, 1970 (effective May 20, 2003), the term of product patents in India was 14
years from the date of issuance. Patents Act (2002 Amendments), Sec. 53.
Accordingly, any patent issued in 1995 or earlier would be expired by 2009.
Based on the data provided by the Controller and Basheer, it appears that few,
if any, Forms 27 were filed prior to 2009. Thus, it is unlikely that any patent
that expired prior to 2009 would have a corresponding Form 27. As a result, for
purposes of counting Forms 27 that were, and should have been filed, we
disregarded 107 patents in our dataset that were issued in 1995 or earlier (the
vast majority of which were owned by Siemens).
[144] A total of 4,935 Forms 27 were identified by
our search. In 2013, Motorola filed 19 Forms 27 that were backdated to 2004 and
2005. These Forms corresponded to patents issued between 2008 and 2010, and
apparently reflected the patentee’s incorrect belief that Form 27 must be filed
as of the date of the filing of a patent application rather than the issuance
of the patent. Because the patentee also filed Forms 27 dated as of 2013 for
these patents, we have disregarded these spurious filings.
[145] Based on the data provided by the Controller
and Basheer, it appears that few, if any, Forms 27 were filed prior to 2009.
Thus, we assumed that Forms 27, if filed, would only have begun to be filed in
2009. As discussed in note 143, supra,
the first patents that could be expected to have a filed Form 27 were issued in
1996 (i.e., one Form filed in 2009, the year of the patent’s expiration). Thus,
beginning with patents issued in 1996, we calculated the total number of Forms
27 that could have been filed with respect to such patents beginning in 2009
and ending in 2016 (noting that we ended our study in August 2016). Thus, for
patents issued in 1996 and expiring in 2009, one Form 27 could have been
filed. For patents issued in 2002 to
2008, and expiring well after 2016, a total of eight Forms 27 could have been
filed, in each case beginning in 2009 and ending in 2016. Patents issued in
2015 could have at most one Form 27 filed. Though Form 27 is not required to be
filed until the year after a patent has been granted, some patentees have made
filings in the year of grant. We counted these filings, but did not count
year-of-grant filings in determining the maximum number of filings that could
be made for a particular patent.
[147] It is not surprising that no forms were
available for patents issued prior to 2007, the first year that the Indian
Controller of Patents drew attention to the Form 27 requirement. See supra Part I.D.
[148] For patents that had different working
designations in Forms 27 filed in different years, we counted a patent to be
declared as worked if at least one Form 27 so designated the patent.
[151] Motorola, Form 27 for 243220, IɴPASS
(Mar. 31, 2014), http://ipindiaonline.gov.in/frm27/2013/243220_2013/243220_2013.pdf.
[152] Ericsson, Form 27 for 241488, IɴPASS
(Feb. 3, 2012), http://ipindiaonline.gov.in/frm27/2011/241488_2011/241488_2011.pdf (“The patentee is in the look out for
appropriate working opportunities in a large scale although there may have been
some use of the patented technology in conjunction with other patented
technologies.”).
[153] Google, Form 27 for 243210, IɴPASS
(Mar. 27, 2015), http://ipindiaonline.gov.in/frm27/2014/243210_2014/243210_2014.pdf. See
infra Part III.D for a discussion of patents as to which the patentee has
changed the working status over the years.
[154] See,
e.g., Ericsson, Form 27 for 209941, IɴPASS (Mar. 30, 2015), http://ipindiaonline.gov.in/frm27/2014/209941_2014/209941_2014.pdf.
[155] See,
e.g., Ericsson, Form 27 for 259809, IɴPASS (Mar. 19, 2015), http://ipindiaonline.gov.in/frm27/2014/259809_2014/259809_2014.pdf.
[156] Ericsson, Form 27 for 227819, IɴPASS
(Mar. 13, 2015), http://ipindiaonline.gov.in/frm27/2014/227819_2014/227819_2014.pdf (“The patentee is in the look out for
appropriate working opportunities in a large scale”); Motorola, Form 27 for
236128, IɴPASS (Mar. 8, 2013), http://ipindiaonline.gov.in/frm27/2012/236128_2012/236128_2012.pdf (“The Patentee is actively looking for
licensees and customers to commercialise the invention in the Indian
environment.”).
[157] Alcatel-Lucent, Form 27 for 258507, IɴPASS
(Mar. 18, 2015), http://ipindiaonline.gov.in/frm27/2014/258507_2014/258507_2014.pdf.
[158] Panasonic, Form 27 for 239668, IɴPASS
(Mar. 21, 2014), http://ipindiaonline.gov.in/frm27/2013/239668_2013/239668_2013.pdf; Panasonic, Form 27 for 208405, IɴPASS
(Mar. 21, 2014), http://ipindiaonline.gov.in/frm27/2013/208405_2013/208405_2013.pdf.
[159] Ericsson, Form 27 for 233994, IɴPASS
(Mar. 6, 2013), http://ipindiaonline.gov.in/frm27/2012/233994_2012/233994_2012.pdf.
[160] Id.
[161] See Oracle, Form 27 for 230190, IɴPASS
(Mar. 24, 2014), http://ipindiaonline.gov.in/frm27/2013/230190_2013/230190_2013.pdf (“The methods/structures of the patent are generally related to
“Asynchronous servers”. This product has been sold to several
businesses in India in the past few years and is believed to be used by them.
Additional information will be enquired and provided to the Patent Office upon
request.”).
[162] Nokia Siemens, Form 27 for 254894, IɴPASS
(Mar. 28, 2014), http://ipindiaonline.gov.in/frm27/2013/254894_2013/254894_2013.pdf.
[163] Ericsson, Form 27 for 249058, IɴPASS
(Mar. 03, 2014), http://ipindiaonline.gov.in/frm27/2013/249058_2013/249058_2013.pdf; In other Forms 27, however, Ericsson
provides
significant detail regarding the standards/specifications covered by its
patents.
See, e.g., Ericsson, Form 27 for 213723, IɴPASS (Mar. 16, 2016), http://ipindiaonline.gov.in/frm27/2015/213723_2015/213723_2015.pdf (citing ETSI TS 126 092 V4.0.0 (2001-03),
ETSI TS 126 073 V4.1.0 (2001-12) and ETSI TS 126 093 V4.0.0 (2000-12), all of
which are pertinent to the UMTS 3G standard).
[164] See,
e.g., Qualcomm, Form 27 for 251876, IɴPASS
(Mar. 28, 2015), http://ipindiaonline.gov.in/frm27/2014/251876_2014/251876_2014.pdf (disclosing Indian licensee Innominds
Software Pvt. Ltd.).
[165] See Ericsson, Form 27 for 213723, IɴPASS
(Mar. 16, 2016), http://ipindiaonline.gov.in/frm27/2015/213723_2015/213723_2015.pdf (referencing royalty payments from Micromax
and Gionee).
[166] Qualcomm, Form 27 for 251876, IɴPASS
(Mar. 28, 2015), http://ipindiaonline.gov.in/frm27/2014/251876_2014/251876_2014.pdf.
[167] Id.
[168]Nokia, Form 27 for 220072, IɴPASS (Mar.
20, 2014), http://ipindiaonline.gov.in/frm27/2013/220072_2013/220072_2013.pdf.
[169] Ericsson, Form 27 for 251757, IɴPASS
(Mar 11, 2014), http://ipindiaonline.gov.in/frm27/2013/251757_2013/251757_2013.pdf.
[170] Id.
[171] See,
e.g., Ericsson, Form 27 for 248764, IɴPASS (Mar. 23, 2012)
[172] See,
e.g., Huawei, Form 27 for 251769, IɴPASS (Mar. 4, 2014), http://ipindiaonline.gov.in/frm27/2013/251769_2013/251769_2013.pdf (“Information not readily available; efforts
will be made to collect and submit further Information, if asked for.”).
[173] See,
e.g., Hitachi, Form 27 for 226462, IɴPASS (Mar. 28, 2013), http://ipindiaonline.gov.in/frm27/2013/226462_2013/226462_2013.pdf (“Confidential Information will be provided
if asked for.”).
[174] Research in Motion, Form 27 for 261068, IɴPASS
(Feb. 10, 2015), http://ipindiaonline.gov.in/frm27/2014/261068_2014/261068_2014.pdf.
[175] Ericsson, Form 27 for 254652, IɴPASS
(Mar. 21, 2016), http://ipindiaonline.gov.in/frm27/2015/254652_2015/254652_2015.pdf.
[176] See,
e.g., Alcatel-Lucent, Form 27 for 202208, IɴPASS (Mar. 27, 2014), http://ipindiaonline.gov.in/frm27/2013/202208_2013/202208_2013.pdf.
[177] See,
e.g., Ericsson, Form 27 for 235605, IɴPASS (Feb. 23, 2011), http://ipindiaonline.gov.in/patentsearch/GrantedSearch/viewdoc.aspx?id=ghLLyAj0oCzH9pUf4tY2Kw%3d%3d&loc=wDBSZCsAt7zoiVrqcFJsRw%3d%3d; Ericsson, Form 27 for 235605, IɴPASS (Feb. 6, 2012), http://ipindiaonline.gov.in/patentsearch/GrantedSearch/viewdoc.aspx?id=ghLLyAj0oCzH9pUf4tY2Kw%3d%3d&loc=wDBSZCsAt7zoiVrqcFJsRw%3d%3d; Huawei, Form 27 for
249244, IɴPASS
(Mar. 11, 2013), http://ipindiaonline.gov.in/patentsearch/GrantedSearch/viewdoc.aspx?id=9BzV82RULJkFoIPZZZeH9A%3d%3d&loc=+mN2fYxnTC4l0fUd8W4CAA%3d%3d.
[179] A patentee may be imprisoned for submitting
false information. The Patents Act, No. 39 of 1970, India Code, § 122 (1970).
[180] See
Reddy & Kadri, supra note 11, at 22; Basheer Writ Petition (2015), supra note 107, at 10 (“authorities have never initiated
action against any of the errant patentees.”).
[182]See supra
Part III.C.3.c.
[183]See supra
Part III.C.3.d.
[184] See
supra Part III.C.3.e.
[185] For example, as of 2015, more than 61,000
patent disclosures had been made against ETSI’s 4G LTE standard, and more than
43,000 against ETSI’s 3G UMTS standard, both of which are only one of many
standards embodied in a typical mobile device. Justus Baron & Tim Pohlmann,
Mapping Standards to Patents Using
Databases of Declared Standard-Essential Patents and Systems of Technological
Classification at 20, Table 5 (Regulation & Econ. Growth, Working
Paper, 2015), http://www.law.northwestern.edu/research-faculty/searlecenter/innovationeconomics/documents/Baron_Pohlmann_Mapping_Standards.pdf.
[186]See supra
Part III.B.
[187] We thank Chris Cotropia for this insight.
[188] 421 Forms 27 were found for Motorola. This
total has been reduced by the 19 Forms filed in 2013 and incorrectly backdated
to 2004 and 2005.
[189] 101 Siemens patents expired prior to 1996.
